Sort Data Frame in R (4 Examples) Order & Rearrange, dplyr & data.table
sort vs. order vs. rank in R (6 Examples) Data, List & by Group Column
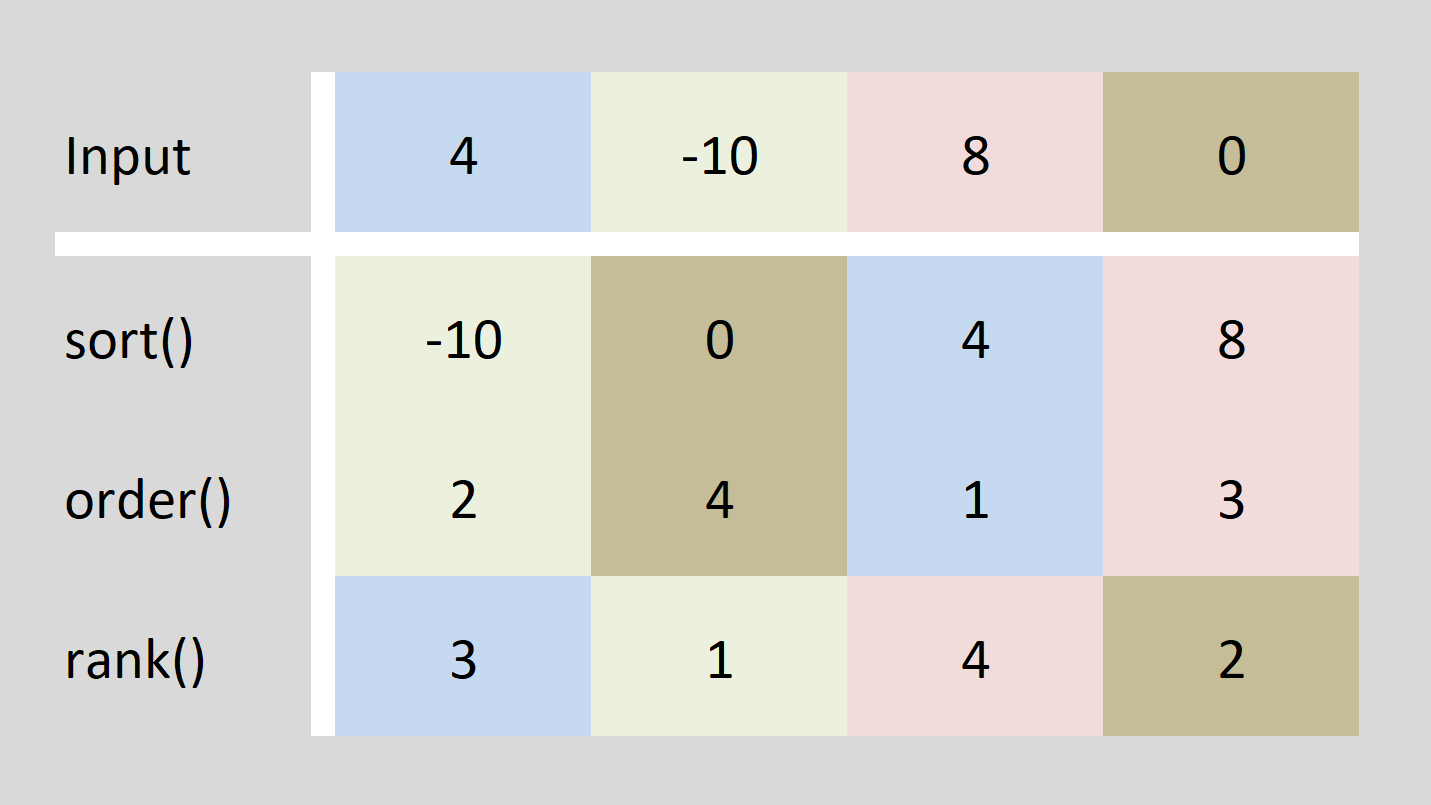
Sorting definition () The sort function in R returns data in ascending or descending order. As seen above, the lowest value (-5) of our sample vector was returned first, followed by the highest value (i.e. 5). Order is defined as () The order function in R returns the ascending or descending position of each element in its input.

R Sort DataFrame Rows by Multiple Columns Spark By {Examples}
A sample of 10 random numbers between 1 to 100 from an array is used. We are going to discuss the following sorting algorithm: Bubble Sort Insertion Sort Selection Sort Merge Sort Quick Sort Bubble Sort In this algorithm, two adjacent elements are compared and swapped if the criteria are met.
[Solved] Merge Sort in R 9to5Answer
Sort (or order) a vector or factor (partially) into ascending or descending order. For ordering along more than one variable, e.g., for sorting data frames, see order. Usage sort (x, decreasing = FALSE,.) # S3 method for default sort (x, decreasing = FALSE, na.last = NA,.)

str_order & str_sort Functions in R (2 Examples) stringr Package
The simplest way to perform sorting in R is by making use of the "order ()" function. Order function allows the user to sort data-frames, matrices, or vectors in ascending or descending manner. In this case, order () will sort the given numbers in ascending order based on their index. Since number 1 is the smallest, it has an index of one.
Data Manipulation in R Find all its concepts at a single place
Details. sort is a generic function for which methods can be written, and sort.int is the internal method which is compatible with S if only the first three arguments are used.. The default sort method makes use of order for classed objects, which in turn makes use of the generic function xtfrm (and can be slow unless a xtfrm method has been defined or is.numeric(x) is true).

R Tutorials Sort [05] and Order YouTube
1 Answer Sorted by: 24 sort () sorts the vector in an ascending order. rank () gives the respective rank of the numbers present in the vector, the smallest number receiving the rank 1. order () returns the indices of the vector in a sorted order. for example: if we apply these functions are applied to the vector - c (3, 1, 2, 5, 4)
Order DataFrame by one descending and one ascending column in R Spark
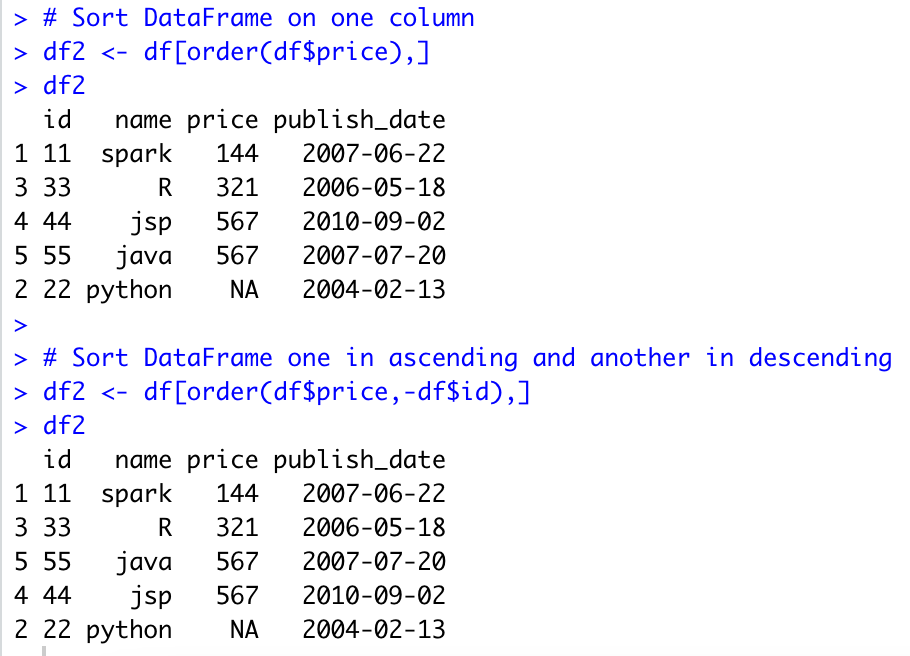
To sort a data frame in R, use the order ( ) function. By default, sorting is ASCENDING. Prepend the sorting variable by a minus sign to indicate DESCENDING order. Here are some examples. Run this code
Arrange, Filter, & Group Rows In R Using dplyr
Sorting a DataFrame allows us to reorder the rows based on the values in one or more columns. This can be useful for various purposes, such as organizing data for analysis or presentation. Methods to sort a dataframe: order () function (increasing and decreasing order) arrange () function from dplyr package

sorting How do I sort points in clockwise order in R with respect to
The basic R syntax of the three functions is the same. However, the output of each function is different. Figure 1 illustrates the functioning of the sort, order, and rank functions: Figure 1: Comparison of sort, order & rank Functions in R. Definition of sort() R function: The sort function returns its input in ascending or descending order.
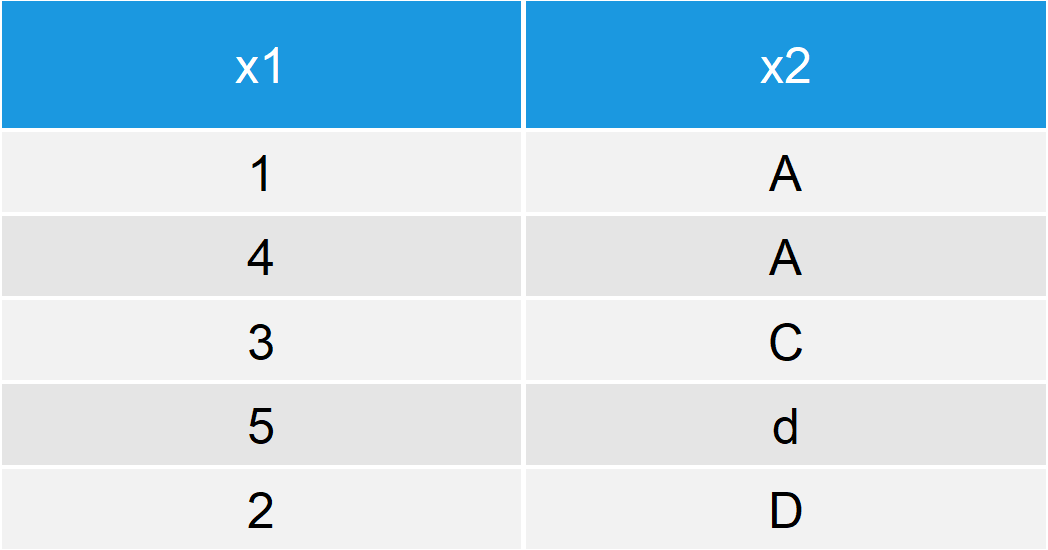
Sort Data Frame in R (4 Examples) Order & Rearrange, dplyr & data.table
In this chapter we will learn how to sort a data frame and vector in R.· Sorting a vector in R can be done with sort function. Sorting a data frame in R can be done with order() function. How to sort in R - sorting a data frame: Lets use mtcars data to describe sorting a data frame in R with order() function. Sort by single column in R:

R Advanced Archives Page 8 of 21 RLang
arrange () orders the rows of a data frame by the values of selected columns. Unlike other dplyr verbs, arrange () largely ignores grouping; you need to explicitly mention grouping variables (or use .by_group = TRUE ) in order to group by them, and functions of variables are evaluated once per data frame, not once per group. Usage

How to Sort Data in R using sort() and order() Functions
There are two methods you can use to sort a table in R: Method 1: Use Base R #sort table in ascending order my_table_sorted <- my_table [order (my_table)] #sort table in descending order my_table_sorted <- my_table [order (my_table, decreasing=TRUE)] Method 2: Use dplyr
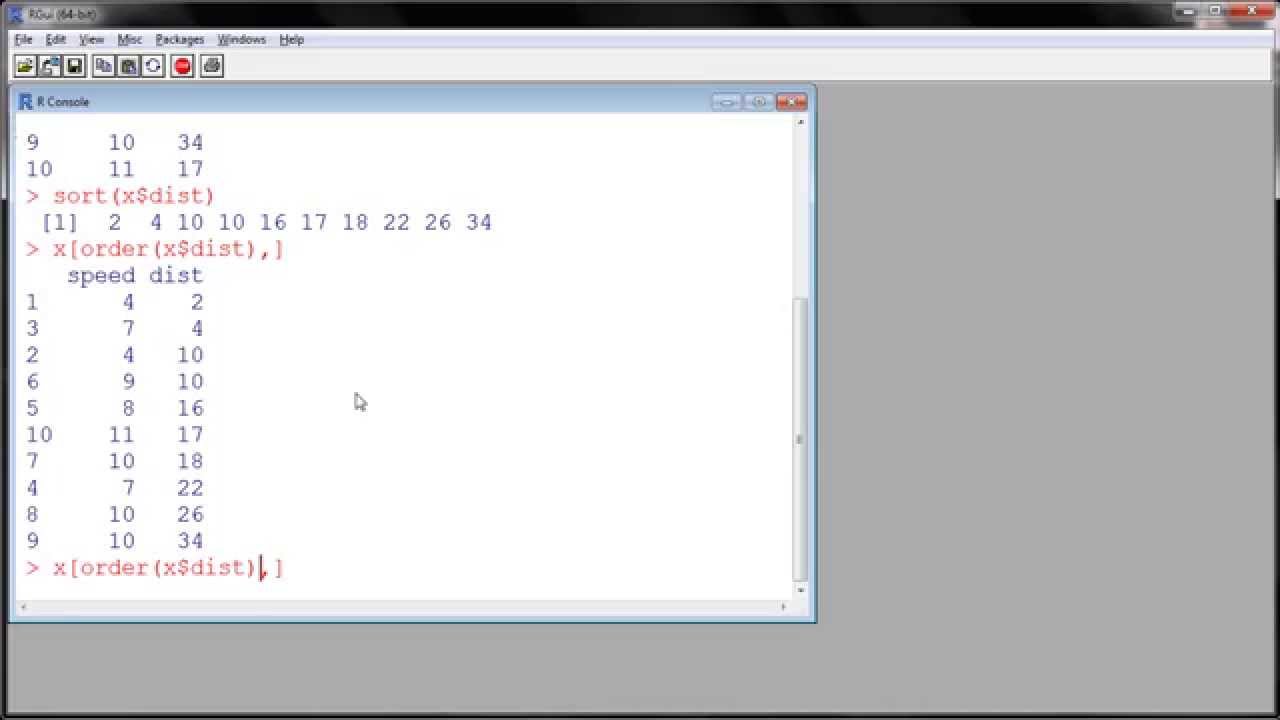
R sort, rank, order YouTube
The following code shows how to use functions from the dplyr package to sort the data frame by points descending (largest to smallest), then by assists ascending: library (dplyr) df %>% arrange( desc (points), assists) team points assists 1 F 99 40 2 C 93 31 3 E 91 34 4 D 91 39 5 B 90 28 6 A 90 33 7 G 85 44
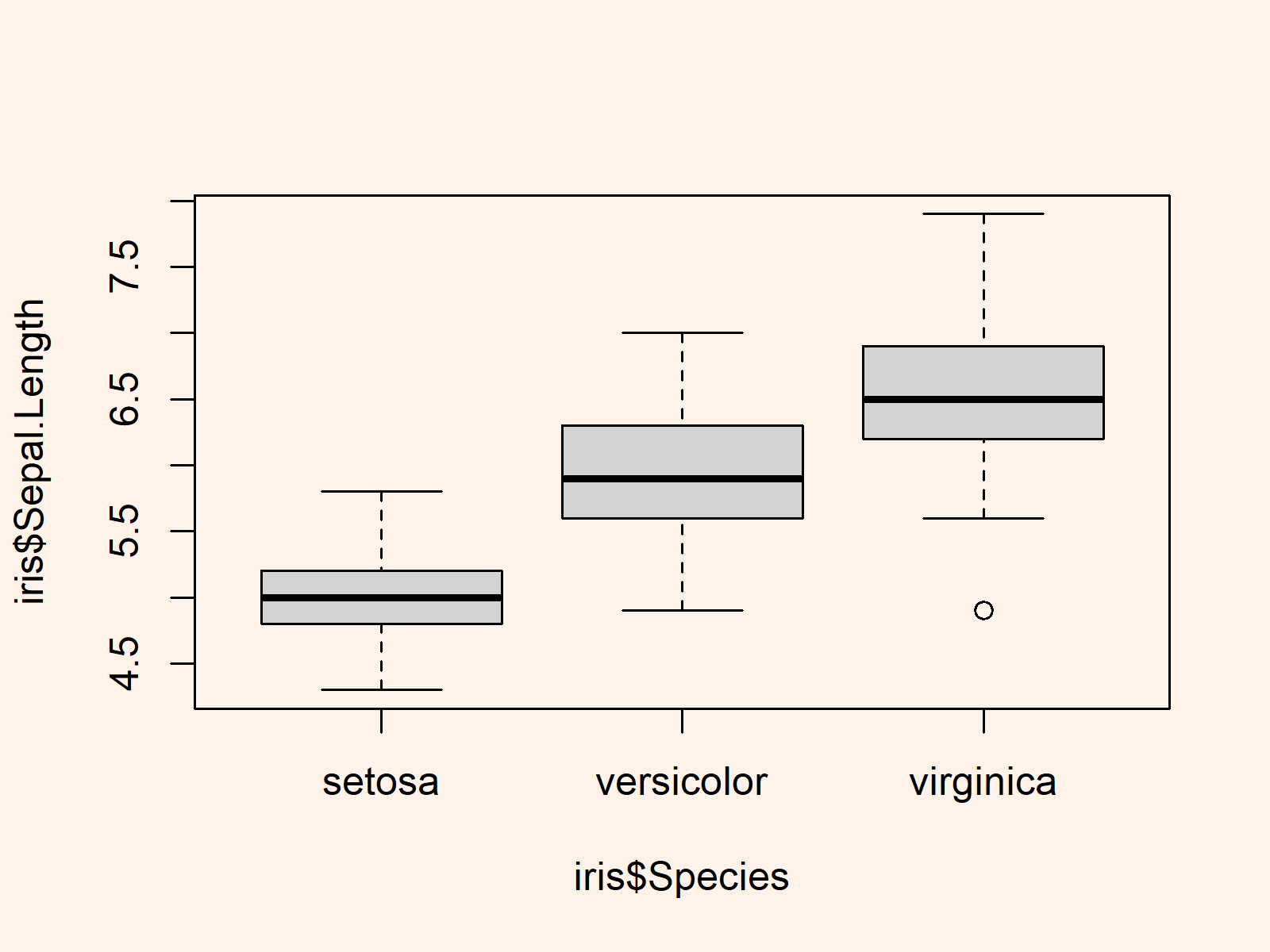
R How to Sort a Boxplot Manually (2 Examples)
R provides a different way to sort the data either in ascending or descending order; Data-analysts, and Data scientists use order (), sort () and packages like dplyr to sort data depending upon the structure of the obtained data.

algorithm Tutorial => Quicksort Basics
Three functions in R that people often get confused are sort, order, and rank. Here's the difference between these functions: sort () will sort a vector in ascending order order () will return the index of each element in a vector in sorted order rank () will assign a rank to each element in a vector (smallest = 1)

How to change the order of bars in bar chart in R ?
There is a function in R that you can use (called the sort function) to sort your data in either ascending or descending order. The variable by which sort you can be a numeric, string or factor variable. You also have some options on how missing values will be handled: they can be listed first, last or removed.